AAQEP Accreditation
Standard 1 Aspect A
Evidence shows that, by the time of program completion, candidates exhibit knowledge, skills, and abilities of professional educators appropriate to their target credential or degree, including the following six (6) aspects: Evidence shows that by the time of program completion, candidates exhibit content, pedagogical, and/or professional knowledge relevant to the credential or degree sought.
The Bilingual Authorization Program (BAP) selected two different measures to examine how it prepares candidates with content, pedagogical, and/or professional knowledge relevant to their preparation as bilingual teacher candidates. The first measure comes from a course assignment for the Spanish (LEE 136) and Hmong (LEE 129) pathways and relevant assignments and the second measure comes from the BAP completer survey.
Data Sources & Analysis
Data Source 1
LEE 135: Spanish Lesson Plan
Description of Data Source:
A key assignment from the LEE 136 course for the Spanish BAP pathway that demonstrates
relevant preparation of Spanish bilingual teachers is creating a Spanish lesson plan
that encompasses the tenets of culturally and linguistically sustaining pedagogy around
a central instructional focus or theme and at least one children’s text. The lesson
plan rubric demonstrates alignment between Common Core State Standards (CCSS) and
language objectives, as well as the learning tasks, and assessments that are related
to an identifiable theme or topic. The central focus takes into account knowledge
of students’ language development, backgrounds, interests, and learning levels that
might further influence students’ thinking and learning. This lesson assignment also
embodies the four (4) learning goals of the course, which include: 1) the impact of
language and culture on teaching and learning in the elementary school, 2) language
acquisition theory, socio-cultural context in teaching and instructional strategies
for Emergent Bilinguals in the classroom, and 3) strategies to promote student success,
including achievement of Common Core state-adopted content and English Language Development
(ELD) standards.
Perspective Captured from Data Source: Faculty
Rationale for using Data Source:
In order to create an effective lesson plan for instruction in Spanish, candidates
have to be able to apply their knowledge of culturally and linguistically sustaining
pedagogy around a central instructional focus or theme, thereby demonstrating their
knowledge of relevant content and pedagogy.
Specific Elements of Data Source: Students’ overall grade on assignment
(Unfortunately, scores were not broken down by rubric criterion, and so holistic scores
must be used)
Definition of Success for Each Element:
Programmatically, our goal was for each candidate to score at least an 8 on this assignment
in order to demonstrate competency.
Displays of Analyzed Data:
Table 1: CLSP lesson plan scores
| User ID | Culturally & Linguistically Sustaining (CLSP) Lesson Plan |
|---|---|
| Student 1 | 10 |
| Student 2 | 10 |
| Student 3 | 9 |
| Student 4 | 10 |
| Student 5 | 9 |
| Student 6 | 8.5 |
| Student 7 | 10 |
| Student 8 | 10 |
| Student 9 | 8 |
| Student 10 | 10 |
| Student 11 | 10 |
| Student 12 | 8.5 |
| Student 13 | 10 |
| Student 14 | 10 |
| Student 15 | 9 |
| Student 16 | 9 |
| Student 17 | 10 |
| Student 18 | 10 |
| Student 19 | 10 |
| Student 20 | 10 |
| Student 21 | 10 |
| Student 22 | 10 |
| Student 23 | 10 |
*Due to changes in program faculty in recent years, unfortunately, only one cycle of data were available.
Interpretation of Data:
Programmatically, our goal was for candidates to attain at least a B average on this
assignment, however, the average for this assignment was a 9.6/10). This demonstrates
that candidates have mastered essential concepts such as establishing strong learning
and language objectives, and alignment among state standards and assessments, as outlined
in the assignment rubric.
It is important to note that, though the above data come from the BAP Spanish pathway, a similar assignment is given in the Hmong pathway. However, again because of changes in program faculty, data from those assignments were not available.
LEE 129 Course Assignment:
The LEE 129 course syllabus for the Hmong BAP pathway is intended to teach the basic content
area in Hmong, which will focus on oral and written communicative skills that are
required for Hmong bilingual teachers. It is also designed to provide new bilingual
classroom teachers with basic content for instruction, development, and evaluation
of teaching materials, and conferencing with parents. Students in this course are
expected to demonstrate knowledge of the Hmong language instruction and to demonstrate
classroom competence in the teaching of oral language development, concepts about
print, reading comprehension, writing skills, spelling and vocabulary development.
“Lesson Projects. You can collect 15 pictures (photographs, magazine cutouts, drawings, etc.) designed to be used for Hmong students in the classroom. Pictures should be accompanied by captions to facilitate learners' language acquisition. Specify the grade level that you will use pictures to teach to. You will also need to choose a picture book. Write a lesson plan to be used with the photos and the chosen picture book. Make sure that your lessons include the different learning modalities: reading, speaking, listening, & writing.”
Data Source 2
BAP Completer Survey
Description of Data Source:
The second measure for standard 1a comes from the BAP completer survey completed by
21 graduates for the spring 2021 term. The purpose for this survey is to understand
graduates' experiences in the BAP and Multiple Subject credential program as well
as employment outcomes. Moving forward, data from this survey will be analyzed and
discussed in the program advisory committee meetings with the purpose of making the
necessary changes to improve the program and to better serve our students and the
interests of stakeholders, such as district partners.
Only one (1) year of completer data is available because this is the first time a completer survey was created and disseminated among program graduates. Prior to the new coordinator’s leadership, the BAP was a very small program and no completer data was collected.
Perspective Captured from Data Source: Program Completer
Rationale for using Data Source:
The survey provides information about the program from the perspective of program
completers who are now in the teaching profession.
Specific Elements of Data Source:
Item 16: The BAP courses helped me gain professional knowledge relevant to my preparation
as a future bilingual/dual immersion teacher
Definition of Success for Each Element:
Completers are asked to rate the extent to which they agree with each statement on
a 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) point Likert scale, with the programmatic
goal being a score of 4.
Displays of Analyzed Data & Interpretation of Data:
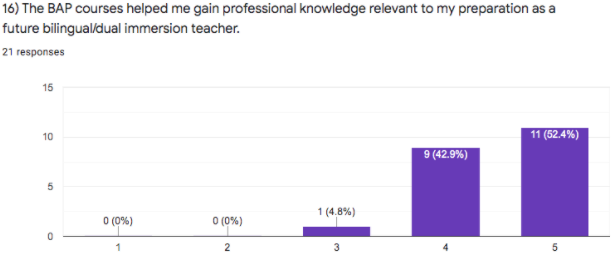
Responses indicate that 52.4% of program completers strongly agree, and 42.9% agree
that the program provided them with the knowledge and skills they need to be bilingual/dual
immersion teachers [BAP completer raw data].
Figure 1:
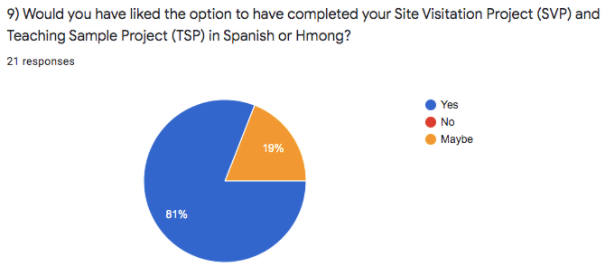
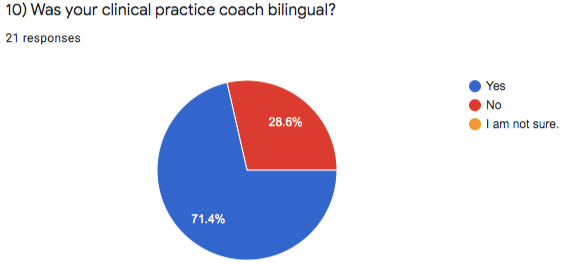
However, program completers did indicate two areas in which the program can improve, which involve their two assessments, the Site Visitation Project and the teaching sample project, as well as their clinical practice coaches. Question 9 asked, “Would you have liked the option to have completed your Site Visitation Project (SVP) and Teaching Sample Project (TSP) in Spanish or Hmong?” The majority of respondents (81%) indicated yes, while 19% indicated maybe. Relatedly, question 10 asked, “Was your clinical practice coach bilingual?” The majority of respondents (71.4%) indicated yes, while 28.6% indicated no.
Figure 2:
Data Analysis and Next Steps:
Analysis of course syllabi, assignments, and completer survey indicate that the BAP
is doing an excellent job in preparing candidates with the content, pedagogical, and/or
professional knowledge relevant to become effective bilingual/dual immersion teachers.
However, two questions from the completer survey also identify needed improvements. At the moment, students do not have the option to complete their SVP and TSP assessments in Spanish or Hmong. This is a target goal that the program will work towards by discussing this topic with the coordinator of the assessments and identifying ways we can accommodate BAP students. Relatedly, since the assessments are scored by clinical practice coaches, it is also a top priority for the program to recruit and hire more Spanish and Hmong bilingual coaches that will be able to effectively assess the growth of students in their bilingual/dual language instruction. This will be done by working closely with the Office of Clinical Practice to assist with efforts in growing the number of districts, schools and classrooms with bilingual/dual immersion programs. These two efforts will be evaluated by surveying BAP students upon entry into the credential program to ensure they have both a bilingual placement and bilingual coach. Program completers will also be surveyed about these two items and a focus group discussion will also take place. Working towards these program goals is a high priority as assessments of language proficiency and subsequent clinical practice support are areas of foci in the California state bilingual authorization standards. Collecting such data at the time of program completion will ensure that the BAP is staying up to date with content, pedagogy, and professional development that aligns with the current guidelines of our state department, field of dual immersion programs, and teacher preparation programs.